https://www.percona.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/A-Guide-to-Better-Understanding-MySQL-Charset-Levels.jpeg We usually receive and see some questions regarding the charset levels in MySQL, especially after the deprecation of utf8mb3 and the new default uf8mb4. If you understand how the charset works on MySQL but have some questions regarding this change, please check out Migrating to utf8mb4: Things to Consider by Sveta Smirnova.Some of the questions […]Planet MySQL
We usually receive and see some questions regarding the charset levels in MySQL, especially after the deprecation of utf8mb3 and the new default uf8mb4. If you understand how the charset works on MySQL but have some questions regarding this change, please check out Migrating to utf8mb4: Things to Consider by Sveta Smirnova.Some of the questions […]Planet MySQL
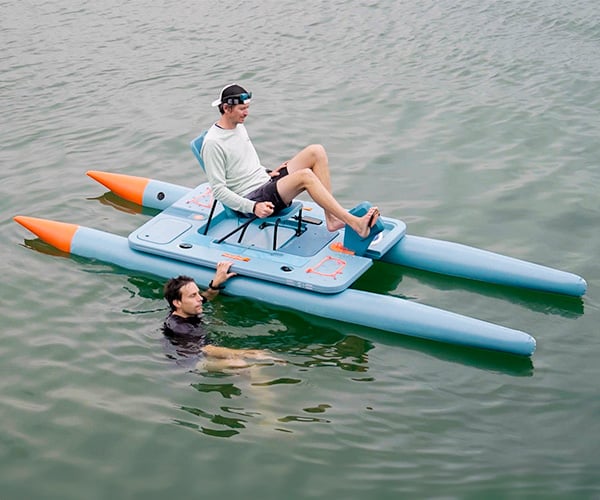
Decathlon X Outercraft HydroBike
https://theawesomer.com/photos/2024/04/decathlon_outercraft_hydrobike_t.jpg
Don’t have the balance to use a stand-up paddleboard? Decathlon teamed up with Outercraft to design the Hydrobike – a unique watercraft that combines a paddleboard, pedal boat, and catamaran. It has inflatable floats, a single-seat, and modular storage for outdoor gear. It’s a proof-of-concept at this point, but we hope to see it go into production.

The Awesomer
Our favorite pictures from the North American eclipse: DPReview Editors’ Challenge results
https://1.img-dpreview.com/files/p/E~C50x0S2000x1500T1200x900~articles/1396158790/DPReview_eclipse_best_02.jpeg
DPReview Editors’ Challenge results
 |
Last week, we issued a challenge to the DPReview community to show us what you got. We wanted to see your best images from the North American total solar eclipse, and over 150 of you submitted!
We saw heaps of creativity and technical know-how on display. It was also interesting to see all the solar flares that matched among photos taken hundreds of miles apart. Before we dive in, a heartfelt thanks to everyone who submitted. We couldn’t call out every image we liked and tried to restrain ourselves as best as possible (otherwise this article would be four times as long). We should also note that images are presented in no particular order other than to provide an engaging visual flow (so we don’t end up with similar back-to-back photos). If you don’t see your work here today, we encourage you to submit for our next challenge. We love seeing your work!
Also, a quick reminder to keep comments constructive and civil. To be blunt, it’s one thing for editors to receive harsh comments, but it’s another threshold to be rude to people not on our staff who want to make some images and share their work. Rule #1: Be nice. That’s it, there is no rule #2.
Plane over eclipse with sunspots seen in Toronto at 02:35 PM EST, by philmar
 |
It’s not only one of the more descriptive titles we saw, but it’s also a great image.
"Shot with a 10 Stop ND filter," philmar writes, "A plane fortuitously passed through the frame. I did notice plane until I reviewed my shots in Lightroom. Toronto experienced 99.95% of the eclipse but was under thick cloud except for about 20 minutes."
Created on Canon EOS R7 at 400mm with adjustments to color temperature, exposure, texture, clarity, vibrance and sharpening.
Untitled, by Morris0
 |
Totality photographed through light clouds in Del Rio, Texas. Morris0 used a Fujifilm X-H2s with a Fujifilm XF 150-600mm lens. They said they previously used this lens to photograph the 2017 eclipse and "knew that the corona fits nicely at 600mm." The photo was also handheld, as Morris0 had left their tripod at home while racing to catch a flight to see the eclipse from a hotel in Del Rio, Texas.
"Experiencing totality is very special as it’s a stunning sight and you feel it get cold, the birds fly to their nests and everyone around expresses emotional outbursts. I was thrilled that we got to see the eclipse and felt that the clouds added to the look and experience."
"Photography is a passion as are nature and wildlife and blending them drives me. I’ve been a member of the DPReview community since about 2000 and have made many friends here. It has been a pleasure sharing my photos and knowledge with the community."
And then the frogs began to sing, by protapic
 |
Captured at the Holden Arboretum in Kirtland, Ohio, given the title, one imagines the false night tricked some amphibians that day. Captured on a Panasonic Lumix DMC-GM1 with Olympus M.Zuiko Digital ED 8-25mm F4 Pro.
Cloudy Eclipse, by Sam Eileen
 |
Taken in Oneonta, NY, using a Canon EOS Rebel T6 (EOS 1300D) with a Canon EF 75-300mm F4.0-5.6 III lens.
"Edited solely in Photoshop 2023. Brightness & Contrast + 15 Slight curves Vibrance & Sat. +35 Smart sharpened w/ 30% noise reduction."
A truly once in a lifetime photo, by cwatson1982
 |
To hear cwatson1982 tell it, this photo was cobbled together through grit and luck.
"We didn’t seriously prepare … I was shooting through an old adapted Nikon 70-210 F4 and a 1.4x teleconverter at 210mm (on a Panasonic Lumix GH6) and using an ND1000 filter," they wrote.
"To be completely honest, I was just shooting bracketed sets on a tripod at regular intervals hoping like most people to get some decent shots of the eclipse. I did not see the birds until after the capture; it was just a very happy accident. I exclaimed ‘what are the odds of that?’ … I kind of feel like I used up all my luck for the year!"
We hope that’s not true cwatson1982. We’re only four months into the year! Wishing you more luck for the year ahead.
Darkness Above, Sunrise all Around, by JMLobert
 |
It’s a thing of beauty when you see a fisheye lens used well.
JMLobert paired a Nikon Z6 with a Sigma 8mm F3.5 EX DG Circular Fisheye and pulled this eclipse image among the trees.
"Venus visible to the right of the sun and Jupiter to the left. While dark above, there is sunrise and sunset all around the viewer, 60 miles out. It’s an eerie and wonderful experience when it suddenly gets dark, temperature drops and the wind stops."
The final image is a composite image made from multiple exposures.
"To accommodate the changing brightness, I bracketed 9 stops every 30 seconds and changed that bracket by 5 stops up, shortly before totality (then back shortly after). Totality is about 12 stops darker than the sunlit day, just a bit short of the 16 stop light loss going from day to night."
solarEclipse-3, by Wakawaka Studios
 |
This scene with backlight clouds was taken just after totality, as the moon moves past the sun. It was taken in Frisco, Texas, with a Canon 5D Mark III and Canon EF 70-200mm F2.8 IS II USM lens.
Several adjustments were made in Lightroom: contrast -3, highlights -41, shadows +100, clarity +80 and sharpened.
eclipse 2024 Ohio, by deoreo
 |
Taking a more environmental approach to the eclipse, deoreo opted for a wide angle Sigma 14-24mm F2.8 DG DN zoom to pair with a Sony a7R IIIa, outside their home in Akron, Ohio.
The best-laid plans, however, presented some challenges. "I completely underestimated how dark totality would be! I managed to get five photos but had to change ISO, f-stop, and shutter on the fly to get this image. The final image was processed with Photoshop
to lighten up the shadows."
Challenges aside, we asked them how they felt about the result. "I’m glad I was able to include my family in the photo. It will be fun to look back on it in the future to remember the moment, and where we were!"
Sanger Eclipse, by Facyn6
 |
It seems this DPReview shutterbug figured who needs lens filters when you can just slap your eclipse-viewing glasses in front of the lens. It feels risky, but the result is rather nice and stands out amid fellow entries.
"I took this photo in the backyard of my home with eclipse glasses in front of the lens," Facyn6 wrote. "Only cropped for better composition. No any other edit."
Eclispe 2024, by Jason333
 |
This was one of the few smartphone entries that caught our eye. It was created at Niagra Falls in Ontario, Canada, and was taken with a Samsung Note 20 Ultra 5G camera.
DLittle, by Phodougrapher
 |
A partial solar eclipse, as seen from cloudy Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada. The image was made with a Nikon 1 V1 with an FT-1 adaptor, Nikon 70-200 and Nikon TC -14E II, for an effective focal length of 756mm. The image has been cropped and resized for sharpness in Adobe RAW.
NJ Eclipse 2024, by Holger Drallmeyer
 |
We’ve seen a strong contingent of submissions from New Jersey in this photo challenge (does DPReview need to make a road trip out?). This submission comes to us from The Garden State, a 1-second exposure of clouds whipsing past the solar show.
Captured with a Canon EOS 6D and Sigma 150 – 500mm F5-6.3 DG OS HSM lens with a 16.5 stop ND Filter. Lightroom adjustments to exposure, highlights and shadows.
Untitled, by scottyinfrisco
 |
Taken with a Panasonic Lumix DMC-FZ2500 using an eclipse filter. "I knew [I] needed the most reach, and this, with digital zoom, was the longest lens I had available."
"The image is SOOC JPEG on Standard Highest quality," wrote scottyinfrisco. "Image is completely unedited."
"I know gear drives this hobby, but never underestimate your own skill in making images."
Great advice and execution, scottyinfrisco; we couldn’t agree more.
Untitled, by Kfsumo
 |
Without a doubt, the most creative submission to the challenge. Kfsumo captured this image with a Ricoh GR III in macro mode pointed at a sheet of colored paper. The shadows on the paper were created holes in a metal umbrella above the paper.
The concept is the centuries-old camera obscure, and the execution is great. Well done!
Untitled, by BaronGreenback
 |
Niagara Falls was under overcast conditions, but BaronGreenback still got a shot of the sun just before or after totality.
Taken on a Nikon D850 with Nikon AF-S Nikkor 200-500mm F5.6E ED VR lens.
Eclipse Stages, by NickMammone
 |
A composite image created from 13 images captures the multiple stages of the eclipse.
NickMammone writes: "While the moment of totality is a spectacular moment, there is a lot more to this event than just those 2 minutes. I wanted to capture that in one picture. This is a combination of multiple photos from different stages of the Eclipse. All shot on the same camera, same lens, same location."
Lightroom edits were made to exposure, contrast, whites, blacks, highlights and color temperature. Level adjustments were also made to each picture to blend the edges into the black background.
Breaking Out from Totality, by dan7901
 |
Solar flares are seen as the moon moves past the sun. Captured in Norwalk, Ohio, along the center of the path for totality, with almost four minutes of darkness.
dan7901 used a Nikon D500 with a Sigma 150-600mmlRig Fluid head AD-01 tripod, all equipment they use as self-described amateur wildlife photographers lens and a Smal. The timing was the biggest challenge they faced.
"In order to catch the solar prominences, I needed to remove the filter before the totality and keep the lens unfiltered for a very short time period after totality."
To help with this, they turned to an app that had countdowns for when the sun would enter and leave totality.
"Since I used the timing app, I really rested myself from taking photos during most of the totality period to enjoin the experience, and after the shots right after leaving the totality, I checked some of the shots, and felt satisfied and released!"
2024 solar eclipse from NJ, by kssharma
 |
Cloud cover is always a concern for eclipse viewing, but kssharma took on the challenge by getting creative. A four-second exposure on their OM System OM-1 yielded this dramatic sky scene over Edison, New Jersey.
"The challenge was how to get an interesting eclipse pics as almost everyone would be taking similar pics," they wrote. "Since I love taking long exposure and my OM-1 allows it handheld I thought to give it a try to make the clouds dramatic instead of using high shutter speed to freeze it." From there, they edited the file to give some definition to the clouds, raise shadows and adjust the tonal curve in Photolab 7.
"Photography is my way to meditate. I love exploring small world around us which we can’t see with our naked eyes. To the DPR I just want to say a huge THANK YOU! DPR itself and the members of the community have been a source of inspiration for me."
Thank you
 |
Thank you to everyone who participated. Seriously, how amazing is it to see our fellow DPReview reader’s work? To see all the entries for yourself and vote for your favorites, head over to the challenge now. The complete shooting specs and gear used for each photo in the challenge platform can also be found in the challenges gallery.
If you couldn’t participate in this editors’ challenge, keep an eye out for our next one. We’ll be doing more during the year as we celebrate 25 years of DPReview. Speaking of which, do you have a suggestion for an Editors’ challenge? In the comments, let us know what to do for our next one.
Articles: Digital Photography Review (dpreview.com)
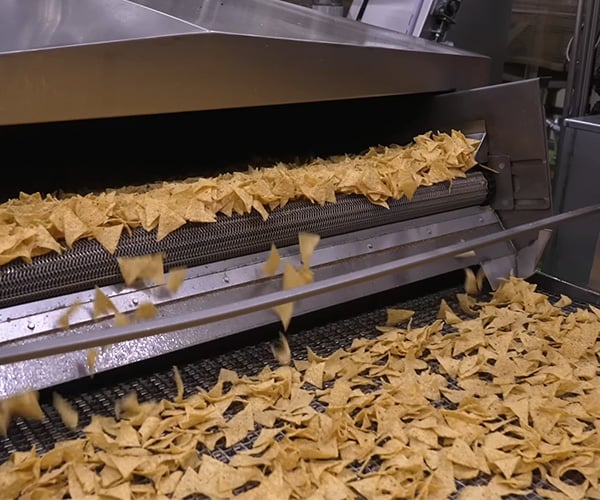
Tortilla Chip Factory
https://theawesomer.com/photos/2024/04/tortilla_chip_factory_t.jpg
Tortilla chips are Mexican food, so it’s a little strange to see a Japanese factory cranking out chips by the millions. Process X visited Koikeya to see how they turn corn kernels into deliciously crunchy snack foods. After boiling corn, machines mash it up into a doughy paste, cut that into triangles, bake and fry those before adding seasonings and packaging.
The Awesomer
23 Famous Magic Trick Secrets Revealed
https://theawesomer.com/photos/2024/04/magic_secrets_revealed_t.jpg
Magic tricks are basically an agreement between the audience and the magician to accept a lie. The Paint Explainer compiled the secrets behind 23 well-known magic tricks and put them all in a single video. While we already knew some of these, like the Statue of Liberty disappearing and the needle-through-the-arm trick, others were new to us.
The Awesomer
Thoughts on how places of worship should handle concealed carry permissions
https://www.buckeyefirearms.org/sites/buckeyefirearms.org/files/styles/slideshow/public/field/image/church-pews.jpg?itok=8Az3o7SE

Editor’s note: The author’s views in this column represent his personal advice for a church carry security team given current Ohio law and the realities of the legal process after a shooting and do not necessarily represent the position of Buckeye Firearms Association.
While the majority of states allow concealed carry in houses of worship, as of April 2024, Ohio is one of only eight states (plus the District of Columbia) that require permission from the church in order to carry a concealed handgun on church property.
Per Ohio Revised Code Section 2923.126, Duties of licensed individual:
(B), a valid license does not authorize the licensee to carry a concealed handgun into any of the following places: …
(6) Any church, synagogue, mosque, or other place of worship, unless the church, synagogue, mosque, or other place of worship posts or permits otherwise.
For the purpose of this article, I will use the word “church” to refer to all.
I work with a number of church safety/security teams, and I’m still surprised at how many church leaders are not clear about what the law states. Even in churches that know the law, I’m told that they suspect a number of people are carrying concealed that have not asked for the church’s permission. The wording of the Ohio statute is only part of what represents “the law.” The law is also defined by how courts rule, how prosecutors interpret, how juries are instructed, and, in the case of churches, how insurers view the intent of the law.
Since April 8, 2004: Buckeye Firearms Association celebrates 20 years of concealed carry in Ohio
In my discussions with church leaders, including some who have had actual shooting incidents, the law is viewed very differently in the aftermath of an incident in which firearms were involved. In fact, I believe that’s the perspective any house of worship should take when deciding what’s the best way to allow concealed carry. Work backward from “as if an incident has occurred” and ask what procedures, paperwork, and training should be in place to address all the questions that will come up in the aftermath.
Let’s start with a simple but important one. Since churches in Ohio must give permission for individuals to carry a concealed handgun, the church should have a written policy for how such requests will be handled to ensure they’re handled responsibly and consistently. It is certainly in the church’s right to have a policy that states no permission will be granted to an individual who requests permission to carry a concealed handgun on church property. But if the church decides that it will grant permission, then the church should have a written policy that outlines a set of criteria the individual will be required to meet. Let me highlight some of those criteria.
In my opinion (and the opinion of wiser people I’ve consulted with), the individual should, as a minimum, meet the following requirements:
- Be a member of the church.
- Have a valid state concealed handgun license.
- Be a member of the church’s safety/security team.
- Pass a state or federal law enforcement handgun qualification test biannually.
When the individual has met these requirements, the church should issue the individual a letter granting the individual permission to carry for no longer than a 12-month period.
Does Ohio law require this letter? No, but as I stated earlier, there are things you do to prepare yourself for how the various parts of the legal system will react given the occurrence of a deadly-force incident.
If the church is going to allow individuals to carry concealed, it should have an organized safety/security team with a leader selected by church leaders, as well as a policy on concealed carry and the use of force that the team operates under. This policy should be reviewed with the church’s insurer to ensure they have no concerns. Such a team should regularly run scenarios at the church to simulate an active-shooter incident, a verbally abusive individual, or a suspicious person. In houses of worship, the team should always remain welcoming yet vigilant.
Keep in mind that active law enforcement officers and retired officers who have maintained their certifications are permitted to carry concealed in a house of worship without asking for the church’s permission. If these individuals are known, the church should encourage them to be members of the safety/security team. They may also be able to provide the team with other skills, such as de-escalation techniques and the use of nonlethal force, such as pepper spray.
If your church has a safety/security team, you should inform local law enforcement that the team exists and ask how to communicate with them if an incident occurs.
As a final thought, if you’re a church leader, please don’t take lightly giving members of your church permission to carry a concealed handgun. It’s not only a significant decision for the church but also for the individual. My prayer is that the individual’s firearms skills will never need to be used, but if they do, the individual and the church will be under intense scrutiny in the aftermath. Having your policies and procedures in order beforehand will prove to be very beneficial when dealing with law enforcement, the legal system, attorneys, and insurers afterward.
Bob Jewell is a firearms instructor in the Cincinnati area. He is a Rangemaster Advanced- and NRA-certified Instructor, a graduate of the Law of Self Defense Instructor Program, and an accomplished tactical shooter. He annually participates in firearms, legal, medical, and self-defense training from top national instructors.
"Keep and Bear Radio" podcast playlist
With host Dean Rieck
Buckeye Firearms Association
This guy fact-checking the “correct way” to eat a cinnamon roll is one reason I love America 😂
https://media.notthebee.com/articles/66140cebd8f8d66140cebd8f8e.jpg
Oh man I absolutely love this.
Not the Bee
Jeffrey Way’s PhpStorm Setup in 2024
https://picperf.io/https://laravelnews.s3.amazonaws.com/featured-images/featured-img-laravel-news-2.png
Call it age. Call it apathy, if you must. I call it contentment. Much of my twenties were spent endlessly experimenting and searching for the perfect editor and workflow. As I read these words back to myself, I’m somewhat embarrassed. “Really? That’s what you spent your twenties doing?” Okay, well, not exclusively. I also like hiking. But, yes, if a new editor hit the market, I was first in line to test it out.
But that was a long time ago. Fast-forward to 2024, and I can’t remember the last time I installed a new code editor. In my eyes, PhpStorm won the IDE wars years ago. The quality and power that they’ve managed to bake into one application is truly staggering.
So, in that spirit, I’d love to share my setup and general workflow with you. As you’ll soon see, the term IDE no longer suggests an incredibly dense UI with hundreds of buttons (though that’s an option, if you prefer). No, I prefer a more minimal approach that I think you’ll appreciate. Okay, let’s do this!
Default Works for Me
When it comes to color themes, it has taken me a decade to realize that one of your IDE’s suggested defaults is usually the way to go. A plugin containing hundreds of themes, each of which misses the mark in some key area, isn’t a great experience. But your editor’s default themes have been battle tested in every possible configuration.
With that in mind, my preference these days is PhpStorm’s Dark theme, combined with their “New UI” (now the default layout).

Similarly, I also stick with the default JetBrains Mono font at 15px. Yes, it seems that age is becoming a recurring theme for this article. Fifteen pixels looks good to me now.

You’ll notice that I’ve also hidden line numbers and tabs. This is of course a personal preference – and a questionable one to many – however, it’s worth experimenting with for a day.
If you’d like to test it out, like all of PhpStorm’s various actions, you can toggle line numbers and tabs using the “Search Anywhere” menu, which defaults to a keybinding of “Shift + Shift.” Search for “line numbers” and “tab placement,” respectively.
For file traversal, I use a combination of the “Search Anywhere” and “Recent Files” menus. Even better, because all of PhpStorm’s file trees allow for instant filtering, I only need to open the “Recent Files” menu and begin typing the first few characters of the file that I want to open. It’s an incredibly fast workflow.

Plugins
When it comes to plugins, the truth is that PhpStorm includes most of what you need straight out of the box. Support for Tailwind CSS, Vue, Pest, Vite, and Node – to name a small handful – are bundled from the start.
As a former Vim user who will never abandon the keybindings that I spent over a year drilling into my finger tips, I do pull in IdeaVim, which is effectively a Vim engine. And if you want to play around with custom UIs and themes, consider installing the Material Theme UI, Nord or Carbon plugins.
But – there’s one incredibly important plugin that deserves its own heading…
Laravel Idea is the Secret Weapon
PhpStorm has a secret weapon that I’ve yet to see any competing editor match. Laravel Idea is a cheap third-party plugin (with a free 30 day trial) that provides an incredibly deep understanding of the Laravel framework.

It provides powerful code generation directly from your editor, Eloquent attribute auto-completion, pre-populated validation rules, smart routing completion, and so much more. Laravel Idea is the only plugin I pay for, and I do it without thinking. It’s that good.
Code Generation
Of course, Laravel and Artisan provide a variety of generators that can be triggered from the command line. However, if you prefer, you can instead run these generators directly within PhpStorm. Navigate to the “Laravel” tab in the menu bar, and choose “Code Generation.”
Here, you can choose your desired file type to generate. It’s so fast.

Notably, when generating an Eloquent model, you’ll be introduced to a dedicated dialog for configuring your desired fields, relations, and options.

Here, I can declare all of the appropriate fields for the model and toggle any companion files that should be generated in the process.
Automatic Validation Rules
Let’s see another example. Imagine that you have an endpoint in your routes file that stores a new Job in the database. Certainly, you should first validate the request data. Rather than writing the rules manually, Laravel Idea can do it for you.
Route::post('/jobs', function () {
request()->validate([
//
]);
});
Place the caret within the validate() array, press Cmd + n, and choose “Add Eloquent Model Fields.” Type the name of the relevant model, Job, and the plugin will populate the array with the appropriate rules, like so:
Route::post('/jobs', function () {
request()->validate([
'employer_id' => ['required', 'exists:employers'],
'title' => ['required'],
'salary' => ['required'],
]);
});
Useful! Laravel Idea provides countless time-savers just like this. It’s an essential plugin for every Laravel user, in my opinion.
Refactor This
The best argument for a dedicated IDE is that you want an editor that deeply understands your underlying language. If I need to rename a variable, implement an interface, or extract a method, I don’t want to rely on regular expressions or a third-party extension. I want that functionality baked into the editor. I want these things working properly to be directly correlated to the financial success of Jetbrains.
If you’re anything like me, you probably have keyboard shortcuts seeping out of your ears at this point. It’s incredible that we can remember so many across a wide range of apps. With that in mind, while there are respective shortcuts for each of PhpStorm’s refactoring options, I use the catch-all “Refactor This” menu, which I bind to Ctrl + t. Open “Search Anywhere” and type “Refactor This” to open the menu manually. This will display a top-level refactoring menu, at which point I can select my preferred refactor.

As always, begin typing to instantly filter the menu items. If I need to, say, extract a method, I would type “extract” and press enter. That way, I never have to reach for the mouse.
An Integrated Terminal
Beginning with the 2024 edition of PHPStorm, you’ll find a new integrated terminal UI that’s significantly improved over previous iterations.

It now supports auto completion, command history (press up), isolated command blocks, and more. I’d recommend binding the integrated Terminal to a shortcut that you’ll remember – I prefer "Ctrl + ` (Backtick)" or Now, you can rapidly toggle the terminal without ever leaving your editor.
Seamless Testing
Testing in PhpStorm is a breeze. Whether you prefer PHPUnit or Pest, it has you covered. Open any test class or file, and you’ll find a Run icon beside each test definition. Give it a click to run that single test in isolation directly inside your editor.

Of course, not every test will pass. For this reason, it can often be useful to re-run the last test from anywhere in your project. This way, you can open a class, make a change, and instantly re-run the failing test to confirm that the issue has been resolved.
The command you want for this behavior is “Rerun.” To avoid touching the mouse, consider assigning a keybinding, such as “Shift + Command + T.”
Tip: You can configure your own keybindings within Settings → Keymap.

In the screenshot above, notice that the commented-out line in Comment.php has triggered a failing test. Let’s fix the issue by uncommenting that line (if only all bugs were this easy to solve), and rerunning the test (using Shift + Command + T).

Wew!
Auto-formatting
PhpStorm of course includes support for automatic code formatting in a variety of code styles. Within the Settings menu, visit Editor → Code Style → PHP and click “Set From” to choose your style.

This is helpful, but if you’d instead prefer an external code formatter such as Laravel Pint, you can easily instruct PhpStorm to disable its internal formatter in favor of your external tool. This is precisely what I do.
Open your Settings menu once again, and visit PHP → Quality Tools. Here, you’ll find a handful of external formatters. Select “Laravel Pint” and you should be all set to go!

Next, it would be nice if we could instruct PhpStorm to perform a series of actions or commands each time we save a file. For example, format the file, optimize the imports (sort and remove unused), clean up the code, run ESLint, etc. This is what the “Actions on Save” menu is for. You can access it within the Settings menu, as usual: Tools → Actions on Save.

Select your preferred actions, and the editor will execute them each time you save a file.
Debugging
Despite what its creator may suggest – 👀 – Xdebug can often be an exercise in frustration to install. It’s clear, though, that the PhpStorm team is well aware of this. They’ve done an excellent job making the process as simple and obvious as possible. Let me show you.
The first stop on your debugging journey is Settings → PHP → Debug. On this page, you’ll see a “Pre-Configuration” checklist to verify that you’ve properly installed Xdebug. Helpful!

This checklist roughly consists of installing Xdebug, choosing a browser toolbar extension, enabling listening for PHP Debug Connections, and then starting a debug session. I would highly suggest using the validator that PhpStorm links to in pre-configuration step one.
Validation Heads Up! If you’re using Herd Pro to automatically detect and enable Xdebug on the fly, PhpStorm’s configuration validator will fail if you simply copy the contents of
phpinfo()directly from the command line (php —info | pbcopy). Instead, signal to Herd that you intend to use Xdebug. One way to do this is by setting a breakpoint. Click inside the gutter for any line number. Next, echophpinfo()and copy its output directly from the browser.

Once you follow each step in the pre-configuration checklist, you should be ready to roll. Set a breakpoint, load the page, and start debugging like the champion you are.

Conclusion
And that’s a wrap!
You may have noticed, but programmers tend to have… opinions. When it comes to code editors, they have even more opinions. Of course, choose the tool that best fits your personality and workflow, but I really do think PhpStorm is worth your time. Having used it for many years at this point, I continue to discover new features and time-savers that I never knew existed.
If I’ve piqued your interest, we have an excellent and free PhpStorm course over at Laracasts. In 2.5 hours, we’ll show you everything you need to know. 🚀

The post Jeffrey Way’s PhpStorm Setup in 2024 appeared first on Laravel News.
Join the Laravel Newsletter to get all the latest Laravel articles like this directly in your inbox.
Laravel News
Jeffrey Way’s PhpStorm Setup in 2024
https://picperf.io/https://laravelnews.s3.amazonaws.com/featured-images/featured-img-laravel-news-2.png
Call it age. Call it apathy, if you must. I call it contentment. Much of my twenties were spent endlessly experimenting and searching for the perfect editor and workflow. As I read these words back to myself, I’m somewhat embarrassed. “Really? That’s what you spent your twenties doing?” Okay, well, not exclusively. I also like hiking. But, yes, if a new editor hit the market, I was first in line to test it out.
But that was a long time ago. Fast-forward to 2024, and I can’t remember the last time I installed a new code editor. In my eyes, PhpStorm won the IDE wars years ago. The quality and power that they’ve managed to bake into one application is truly staggering.
So, in that spirit, I’d love to share my setup and general workflow with you. As you’ll soon see, the term IDE no longer suggests an incredibly dense UI with hundreds of buttons (though that’s an option, if you prefer). No, I prefer a more minimal approach that I think you’ll appreciate. Okay, let’s do this!
Default Works for Me
When it comes to color themes, it has taken me a decade to realize that one of your IDE’s suggested defaults is usually the way to go. A plugin containing hundreds of themes, each of which misses the mark in some key area, isn’t a great experience. But your editor’s default themes have been battle tested in every possible configuration.
With that in mind, my preference these days is PhpStorm’s Dark theme, combined with their “New UI” (now the default layout).

Similarly, I also stick with the default JetBrains Mono font at 15px. Yes, it seems that age is becoming a recurring theme for this article. Fifteen pixels looks good to me now.

You’ll notice that I’ve also hidden line numbers and tabs. This is of course a personal preference – and a questionable one to many – however, it’s worth experimenting with for a day.
If you’d like to test it out, like all of PhpStorm’s various actions, you can toggle line numbers and tabs using the “Search Anywhere” menu, which defaults to a keybinding of “Shift + Shift.” Search for “line numbers” and “tab placement,” respectively.
For file traversal, I use a combination of the “Search Anywhere” and “Recent Files” menus. Even better, because all of PhpStorm’s file trees allow for instant filtering, I only need to open the “Recent Files” menu and begin typing the first few characters of the file that I want to open. It’s an incredibly fast workflow.

Plugins
When it comes to plugins, the truth is that PhpStorm includes most of what you need straight out of the box. Support for Tailwind CSS, Vue, Pest, Vite, and Node – to name a small handful – are bundled from the start.
As a former Vim user who will never abandon the keybindings that I spent over a year drilling into my finger tips, I do pull in IdeaVim, which is effectively a Vim engine. And if you want to play around with custom UIs and themes, consider installing the Material Theme UI, Nord or Carbon plugins.
But – there’s one incredibly important plugin that deserves its own heading…
Laravel Idea is the Secret Weapon
PhpStorm has a secret weapon that I’ve yet to see any competing editor match. Laravel Idea is a cheap third-party plugin (with a free 30 day trial) that provides an incredibly deep understanding of the Laravel framework.

It provides powerful code generation directly from your editor, Eloquent attribute auto-completion, pre-populated validation rules, smart routing completion, and so much more. Laravel Idea is the only plugin I pay for, and I do it without thinking. It’s that good.
Code Generation
Of course, Laravel and Artisan provide a variety of generators that can be triggered from the command line. However, if you prefer, you can instead run these generators directly within PhpStorm. Navigate to the “Laravel” tab in the menu bar, and choose “Code Generation.”
Here, you can choose your desired file type to generate. It’s so fast.

Notably, when generating an Eloquent model, you’ll be introduced to a dedicated dialog for configuring your desired fields, relations, and options.

Here, I can declare all of the appropriate fields for the model and toggle any companion files that should be generated in the process.
Automatic Validation Rules
Let’s see another example. Imagine that you have an endpoint in your routes file that stores a new Job in the database. Certainly, you should first validate the request data. Rather than writing the rules manually, Laravel Idea can do it for you.
Route::post('/jobs', function () {
request()->validate([
//
]);
});
Place the caret within the validate() array, press Cmd + n, and choose “Add Eloquent Model Fields.” Type the name of the relevant model, Job, and the plugin will populate the array with the appropriate rules, like so:
Route::post('/jobs', function () {
request()->validate([
'employer_id' => ['required', 'exists:employers'],
'title' => ['required'],
'salary' => ['required'],
]);
});
Useful! Laravel Idea provides countless time-savers just like this. It’s an essential plugin for every Laravel user, in my opinion.
Refactor This
The best argument for a dedicated IDE is that you want an editor that deeply understands your underlying language. If I need to rename a variable, implement an interface, or extract a method, I don’t want to rely on regular expressions or a third-party extension. I want that functionality baked into the editor. I want these things working properly to be directly correlated to the financial success of Jetbrains.
If you’re anything like me, you probably have keyboard shortcuts seeping out of your ears at this point. It’s incredible that we can remember so many across a wide range of apps. With that in mind, while there are respective shortcuts for each of PhpStorm’s refactoring options, I use the catch-all “Refactor This” menu, which I bind to Ctrl + t. Open “Search Anywhere” and type “Refactor This” to open the menu manually. This will display a top-level refactoring menu, at which point I can select my preferred refactor.

As always, begin typing to instantly filter the menu items. If I need to, say, extract a method, I would type “extract” and press enter. That way, I never have to reach for the mouse.
An Integrated Terminal
Beginning with the 2024 edition of PHPStorm, you’ll find a new integrated terminal UI that’s significantly improved over previous iterations.

It now supports auto completion, command history (press up), isolated command blocks, and more. I’d recommend binding the integrated Terminal to a shortcut that you’ll remember – I prefer "Ctrl + ` (Backtick)" or Now, you can rapidly toggle the terminal without ever leaving your editor.
Seamless Testing
Testing in PhpStorm is a breeze. Whether you prefer PHPUnit or Pest, it has you covered. Open any test class or file, and you’ll find a Run icon beside each test definition. Give it a click to run that single test in isolation directly inside your editor.

Of course, not every test will pass. For this reason, it can often be useful to re-run the last test from anywhere in your project. This way, you can open a class, make a change, and instantly re-run the failing test to confirm that the issue has been resolved.
The command you want for this behavior is “Rerun.” To avoid touching the mouse, consider assigning a keybinding, such as “Shift + Command + T.”
Tip: You can configure your own keybindings within Settings → Keymap.

In the screenshot above, notice that the commented-out line in Comment.php has triggered a failing test. Let’s fix the issue by uncommenting that line (if only all bugs were this easy to solve), and rerunning the test (using Shift + Command + T).

Wew!
Auto-formatting
PhpStorm of course includes support for automatic code formatting in a variety of code styles. Within the Settings menu, visit Editor → Code Style → PHP and click “Set From” to choose your style.

This is helpful, but if you’d instead prefer an external code formatter such as Laravel Pint, you can easily instruct PhpStorm to disable its internal formatter in favor of your external tool. This is precisely what I do.
Open your Settings menu once again, and visit PHP → Quality Tools. Here, you’ll find a handful of external formatters. Select “Laravel Pint” and you should be all set to go!

Next, it would be nice if we could instruct PhpStorm to perform a series of actions or commands each time we save a file. For example, format the file, optimize the imports (sort and remove unused), clean up the code, run ESLint, etc. This is what the “Actions on Save” menu is for. You can access it within the Settings menu, as usual: Tools → Actions on Save.

Select your preferred actions, and the editor will execute them each time you save a file.
Debugging
Despite what its creator may suggest – 👀 – Xdebug can often be an exercise in frustration to install. It’s clear, though, that the PhpStorm team is well aware of this. They’ve done an excellent job making the process as simple and obvious as possible. Let me show you.
The first stop on your debugging journey is Settings → PHP → Debug. On this page, you’ll see a “Pre-Configuration” checklist to verify that you’ve properly installed Xdebug. Helpful!

This checklist roughly consists of installing Xdebug, choosing a browser toolbar extension, enabling listening for PHP Debug Connections, and then starting a debug session. I would highly suggest using the validator that PhpStorm links to in pre-configuration step one.
Validation Heads Up! If you’re using Herd Pro to automatically detect and enable Xdebug on the fly, PhpStorm’s configuration validator will fail if you simply copy the contents of
phpinfo()directly from the command line (php —info | pbcopy). Instead, signal to Herd that you intend to use Xdebug. One way to do this is by setting a breakpoint. Click inside the gutter for any line number. Next, echophpinfo()and copy its output directly from the browser.

Once you follow each step in the pre-configuration checklist, you should be ready to roll. Set a breakpoint, load the page, and start debugging like the champion you are.

Conclusion
And that’s a wrap!
You may have noticed, but programmers tend to have… opinions. When it comes to code editors, they have even more opinions. Of course, choose the tool that best fits your personality and workflow, but I really do think PhpStorm is worth your time. Having used it for many years at this point, I continue to discover new features and time-savers that I never knew existed.
If I’ve piqued your interest, we have an excellent and free PhpStorm course over at Laracasts. In 2.5 hours, we’ll show you everything you need to know. 🚀

The post Jeffrey Way’s PhpStorm Setup in 2024 appeared first on Laravel News.
Join the Laravel Newsletter to get all the latest Laravel articles like this directly in your inbox.
Laravel News
Scientists Find Evidence in Mice That Inherited Alzheimer’s Could Be Transmittable
https://i.kinja-img.com/image/upload/c_fill,h_675,pg_1,q_80,w_1200/f936d268d68437f8339f234f95c9eca6.jpg
A new study this week points to a potential transmission risk of Alzheimer’s disease. Researchers found evidence in mice that an inherited form of the neurological disorder can be passed on via bone marrow donation. While such a danger has yet to be confirmed in humans and likely to be infrequent if it can happen, the authors say more research has to be done to investigate the possibility.
Rebecca Hall on Filming Godzilla x Kong: The New Empire
The research was led by scientists from the University of British Columbia. They were interested in studying cells that produce something known as the amyloid precursor protein (APP)—proteins that seem to have several important functions but can also be turned into amyloid beta, a protein thought to play a driving role in causing Alzheimer’s disease. In those with Alzheimer’s, a misfolded and damaging version of amyloid beta accumulates in the brain, eventually forming into clumped-together deposits called plaques (a similar process occurs with the tau protein).
Most cases of Alzheimer’s are caused by multiple factors working together, such as age-related changes in the brain. But there are known inherited mutations that can make someone much more likely to develop it, usually at an earlier age than normal. Some of these mutations involve the gene that regulates APP production in cells. APP-producing cells aren’t just found in the brain, though, but throughout the body, including within our bone marrow. So the authors, led by immunologist Wilfred Jefferies, were curious about the potential of these outside cells to cause Alzheimer’s as well.
“We wondered, therefore, whether a familial form of Alzheimer’s disease could be initiated in a mouse after injection of the bone marrow from an afflicted mouse into the bloodstream of a normal mouse,” Jefferies told Gizmodo in an email.
The team first bred mice carrying a defective version of the APP gene found in humans, one that would ensure their development of Alzheimer’s. Then they transplanted bone marrow from these mice to two other groups of mice: mice with a normal APP gene and mice bred to have no APP gene at all. Following the transplantation, both groups of mice developed symptoms of cognitive impairment and clear signs of Alzhemer’s, such as plaque build-up in the brain. Those without the APP gene became sick quicker than expected, however, showing symptoms at six months old on average (both the original and normal APP-carrying mice began to show symptoms around nine months).
The findings, published Thursday in Stem Cell Reports, appear to demonstrate that “the mutated gene in the donor cells can transfer and cause” Alzheimer’s, Jefferies said. And while the mice without APP became sicker faster, the results suggest that even healthy individuals could be at risk from this route of infection.
Other scientists have found evidence that Alzheimer’s can be transmitted between people, though only under very rare and specific conditions, such as the donation of contaminated human growth hormone extracted from cadaver brains (a practice long since ended). And if there is a real transmission risk of familial Alzheimer’s via bone marrow transplantation, it’s likely to be low.
But based on their findings, the authors do “urge further investigation of this phenomenon,” Jeffries said. “We also advocate that human donors of blood, tissue, organ, and stem cells should be screened to prevent the inadvertent transfer of disease during blood product transfusions and cellular therapies.”
The authors plan to keep looking into the matter themselves. They would like to better understand exactly how these donated APP-producing stem cells, which can only turn into blood cells or platelets, not neurons, go on to trigger Alzheimer’s. They also hope to study whether other types of transplantation can transmit the disease or whether it’s possible to treat Alzheimer’s by transplanting normal cells to those afflicted with the condition; early animal trials involving stem cells have found some promising results for this approach.
Gizmodo