https://www.louderwithcrowder.com/media-library/eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJpbWFnZSI6Imh0dHBzOi8vYXNzZXRzLnJibC5tcy8yNzE0MzQ4MS9vcmlnaW4uanBnIiwiZXhwaXJlc19hdCI6MTYzMTY3MDYzMX0.3LksOvClMIP_Aqe7Iy3mGNAE2gWp8-4fYS94RaOOlh0/image.jpg?width=980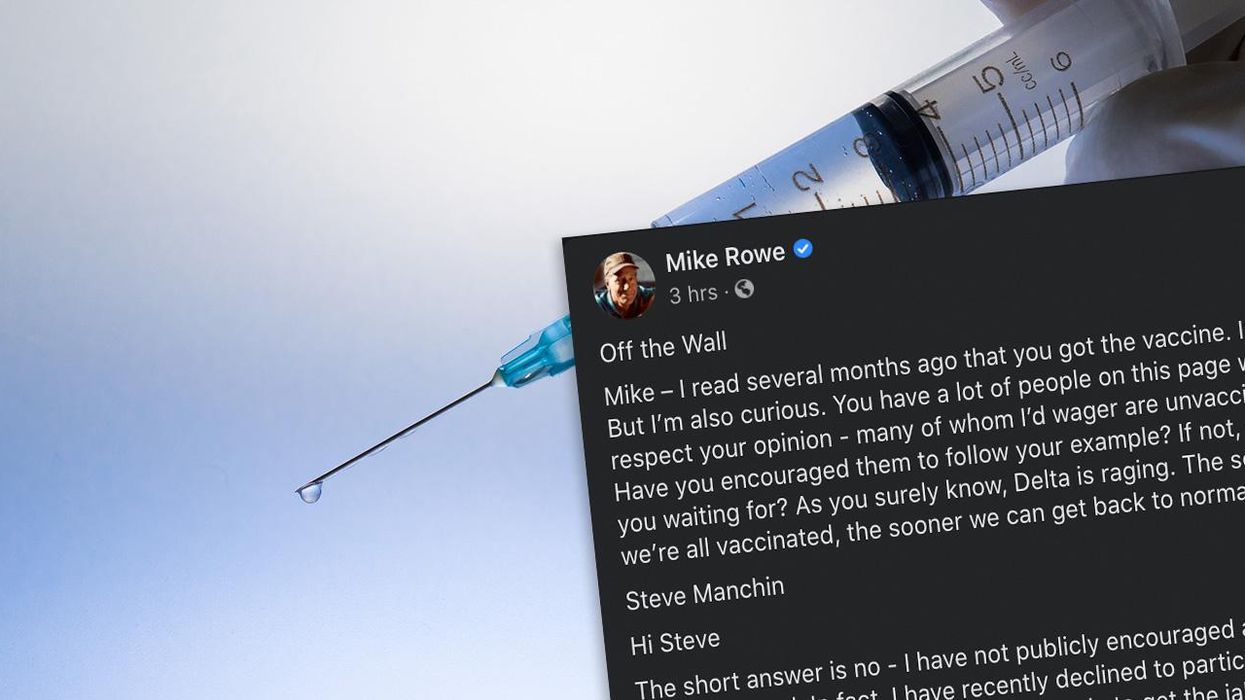
The Holy Vaccinated Saints are some of the most insufferable nimrods out there. I know we make fun of "Karens" but we need to expand and come up with some kind of denigrating moniker for the lot of them. One such pro-vaccine nimrod wrote into Mike Rowe, encouraging Mike to use the power of his influence to spread the Gospel according to Fauci. My words, "Steve" isn’t near clever enough to think up something half-way original. Not his fault, he was born a sheep. Anyway, Mike Rowe didn’t take the guilt bait, and instead of saying "no thanks, to each their own" he wrote a brilliant, spicy essay that every politico and their minions pushing the pokey should read and absorb. They won’t, but a girl can dream.
You’d need to click the "See More" link to read the full post, and you absolutely should, it’s Mike Rowe at his best. But a few of you might be on a social media hiatus or you, blessedly, told Facebook to go pound sand. I approve. If that be the case, here is my favorite chunk from Mike’s post:
"The fact is, millions of reasonable Americans have every right to feel confused and skeptical. Those people you refer to, Steve – the ones now telling us that we can "get back to normal just as soon as everyone is vaccinated" – those are the same people who said, "two weeks to flatten the curve!" Those are the same people who told us that masks were "useless" before they told us they were "critical." Those are the same people who told us that a return to normalcy would occur just as soon as "the most vulnerable" among us were vaccinated. Then, just as soon as "half the population" was vaccinated. Then, just as soon as we achieved "herd immunity." Those are the same people who told us they wouldn’t trust ANY vaccine developed under the last administration. Now, those very same people are belittling the skeptics!
If this were a Peanuts cartoon, those people would be Lucy, pulling away the football at the last moment while a nation full of Charlie Browns land flat on their collective back, over and over and over again. Those people you refer to – elected officials, journalists, and most disturbingly, more than a few medical experts – have moved the goalposts time and time again, while ignoring the same rules and restrictions they demand we all live by. They’re always certain, usually wrong, incapable of shame, and utterly void of humility. Is it any wonder millions find them unpersuasive?"
Mike is, as usual, right about this. A lot of us are skeptical. Speaking for myself, I cannot nor will I trust anyone in government to make my decisions. I make my decisions, and I make my own decisions better than an elected official and better than a butt-kissing sycophant who elected those assholes. I pride myself on critical thinking skills that I saw few people exercising at the start of the pandemic way back in February of 2020. What I did see was herd mentality in full swing. Plenty of right-leaning leaders went right along with it, too.
It’s good to be skeptical. It’s good to hit pause. Sometimes going with the herd is the right move. Sometimes it’s not. But that’s where thinking comes into play rather than just feeling and reacting to those feelings. Or in the case of much of the COVID panic, reacting to what others are feeling and saying so forcefully.
It’s your body and your choice. Remember that line? If you decide the vaccine is right for you, no one is stopping you. But some people have decided it’s not right for them. It isn’t up to you or anyone else to force them to do something they do not want to do to their body. Hard stop.
I have to add this last part, because it resonated with me:
At this point, I’m afraid the the government has but one course of sensible action – get the FDA on board, stat, and then, provide an honest, daily breakdown of just how quickly the virus is spreading among the unvaccinated, versus the vaccinated. No more threats, no more judgments, no more politics, no more celebrity-driven PSA’s, no more ham-fisted attempts at public shaming. Just a steady flow of verifiable data that definitively proves that the vast, undeniable, overwhelming majority of people who get this disease are unvaccinated. In other words, give us the facts, admit your mistakes, try on a bit of humility, and stop treating the unvaccinated like the enemy.
This is the gold: "no more ham-fisted attempts at public shaming" and "stop treating the unvaccinated like the enemy."
I’m tired of the vaccinated treating the unvaccinated like second class citizens. Or third class. Vermin, maybe. It’s gone on long enough and it’s gross. Hopefully those of us in the conservative crowd have been consistent in saying you need to do what you need to do, and so long as others are not negatively affected, fine. But man, the vaccinated people are teetering on the edge of becoming just as if not more obnoxious than the BAKE ME A CAKE, BIGOT Gaystapo soldiers.
Thanks for the wisdom, Mike. Hopefully it’ll resonate with the obnoxious vaccinated populace.
Get your content free from Big Tech’s filter. Bookmark this website and sign up for our newsletter!
Louder With Crowder