https://blog.meilisearch.com/content/images/size/w1200/2023/11/laravel_meili_test.jpg
In this guide, we will see how to use the search functionality in Laravel 10. We’ll start with by introducing the benefits of full-text search. Then, we’ll walk you through setting up full-text search in your Laravel application.
Why use full-text search?
In traditional SQL or NoSQL databases, queries find results exactly matching given criteria. Conversely, full-text search queries can match some or all of a text query with the database’s content. So essentially, full-text search can provide results even in case of partial matches.
When building user-facing search interfaces, full-text search is empowering for users. Tolerance to typos, prefix search, and synonyms help them get results more quickly. It improves discoverability when users do not know what they’re looking for.
How to use search functionality in Laravel 10?
Installing Laravel Scout
Laravel comes with out-of-the-box full-text search capabilities via Laravel Scout.
To enable it, navigate to your Laravel application directory and install Scout via the Composer package manager:
composer require laravel/scoutAfter installing Scout, you should publish the Scout configuration file. You can do this by running the following artisan command:
php artisan vendor:publish --provider="Laravel\Scout\ScoutServiceProvider"This command should create a new configuration file in your application directory: config/scout.php.
Configuring the Laravel Scout driver
Let’s configure Laravel Scout to use the Meilisearch driver. Meilisearch is an open-source search engine built in Rust. This will allow to get the best full-text search performance. Indeed, the database driver comes with limitations inherent to SQL databases.
First, install the dependencies required to use Scout with Meilisearch via Composer:
composer require meilisearch/meilisearch-php http-interop/http-factory-guzzleThen, update the environment variables in your .env file:
SCOUT_DRIVER=meilisearch
# Use the host below if you're running Meilisearch via Laravel Sail
MEILISEARCH_HOST=http://meilisearch:7700
MEILISEARCH_KEY=masterKeyLaravel’s official Docker development environment, Laravel Sail, comes with a Meilisearch service out-of-the-box. Please note that when running Meilisearch via Sail, Meilisearch’s host is http://meilisearch:7700.
For production use cases, we recommend using a managed Meilisearch via Meilisearch Cloud. On Meilisearch Cloud, you can find your host URL in your project settings.
Making Eloquent models searchable
With Scout installed and configured, just add the Laravel\Scout\Searchable trait to your Eloquent models to make them searchable. This trait will use Laravel’s model observers to keep the data in your model in sync with Meilisearch.
Here’s an example model:
<?php
namespace App\Models;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
use Laravel\Scout\Searchable;
class Contact extends Model
{
use Searchable;
}You can use the toSearchableArray method to configure which fields to store in Meilisearch. This notably enables storing a model and its relationships’ data in the same document.
The example below shows how to store a model’s relationships data in Meilisearch:
<?php
namespace App\Models;
use App\Models\Company;
use Laravel\Scout\Searchable;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Relations\BelongsTo;
class Contact extends Model
{
use Searchable;
public function company(): BelongsTo
{
return $this->belongsTo(Company::class);
}
public function toSearchableArray(): array
{
// All model attributes are made searchable
$array = $this->toArray();
// Then we add some additional fields
$array['organization_id'] = $this->company->organization->id;
$array['company_name'] = $this->company->name;
$array['company_url'] = $this->company->url;
return $array;
}
}
Configuring filterable and sortable attributes
Meilisearch allows you to perform advanced filtering and sorting on your search results. Choose which attributes are filterable and sortable via your Meilisearch index settings.
Configure your Meilisearch index settings via the config/scout.php file:
<?php
use App\Models\Contact;
return [
// additional configuration...
'meilisearch' => [
'host' => env('MEILISEARCH_HOST', 'http://localhost:7700'),
'key' => env('MEILISEARCH_KEY'),
'index-settings' => [
Contact::class => [
'filterableAttributes' => ['organization_id'],
'sortableAttributes' => ['name', 'company_name']
],
],
],The example above updates Meilisearch index settings for the Contact model:
- it makes the
organization_idfield filterable - it makes the
nameandcompany_namefields sortable
Update your Meilisearch index settings by running the following Artisan command:
php artisan scout:sync-index-settingsLaravel full-text search example
We built a demo application to give you a feel of what full-text search looks like in a Laravel application. This demo showcases an app-wide search in a CRM (Customer Relationship Management) application.
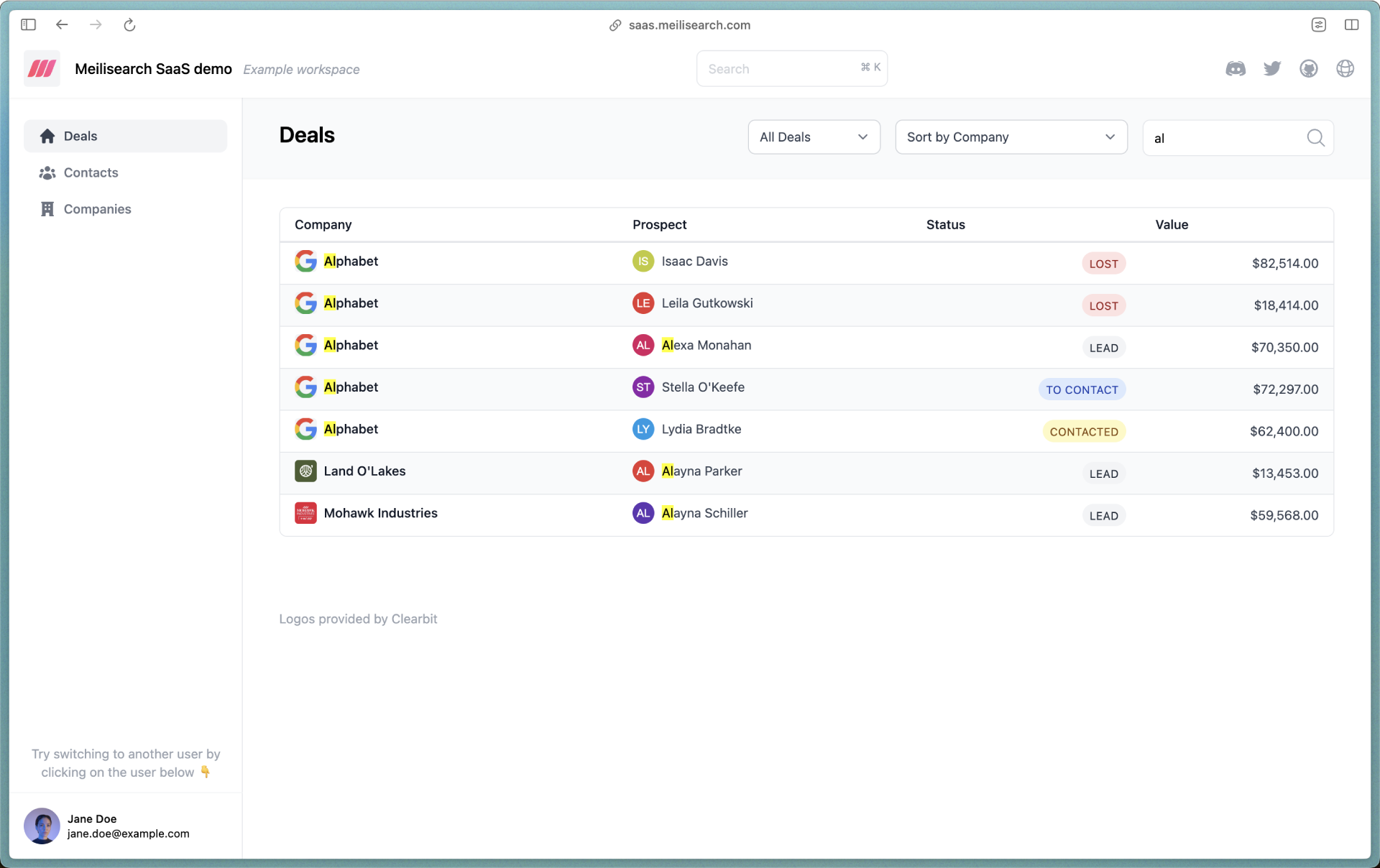
This demo application uses the following search features:
The code is open-sourced on Github. ????
???? Check out the repository: https://github.com/meilisearch/saas-demo
We hope this guide helped to understand the importance of full-text search and how to implement it with Laravel. For more information, read the Laravel Scout and Meilisearch docs.
Meilisearch is an open-source search engine with intuitive developer experience to build user-facing search. You can self-host it or get a premium experience with Meilisearch Cloud.
For more things Meilisearch, you can join the community on Discord or subscribe to the newsletter. You can learn more about the product by checking out the roadmap and participating in product discussions.
Laravel News Links











