https://media.notthebee.com/articles/664b4d1a72f68664b4d1a72f69.jpg
What a show!
Not the Bee
Just another WordPress site
https://media.notthebee.com/articles/664b4d1a72f68664b4d1a72f69.jpg
What a show!
Not the Bee
https://orasites-prodapp.cec.ocp.oraclecloud.com/content/published/api/v1.1/assets/CONTFB2A013CF4E04D7CA51DEF059A3B29C1/Medium?cb=_cache_8547&format=jpg&channelToken=32954b2a813146c9b9a4fa99364eba8eThis blog post illustrates how to use AutoML on MySQL Heatwave to train an optimized machine learning model to forecast crimePlanet MySQL
https://opengraph.githubassets.com/e30fd86d88c35638554c4ad7cf952799e4016e6a866e7f8117380180326bf698/TheDragonCode/laravel-actions/releases/tag/5.0.0
Laravel News Links
https://blog.finxter.com/wp-content/plugins/wp-youtube-lyte/lyteCache.php?origThumbUrl=https%3A%2F%2Fi.ytimg.com%2Fvi%2FLc0mYwAmoiw%2F0.jpg

Step 1: Visit the Yahoo Finance website of the stock you want to analyze. In my case, it was the NVIDIA and GOOGLE stocks.
 https://finance.yahoo.com/quote/NVDA/key-statistics
https://finance.yahoo.com/quote/NVDA/key-statistics
Step 2: Take a screenshot of the statistics tab using the screencapture software of your choice. Save everything including the non-visible parts of the page:

Step 3: Paste the screenshot into your ChatGPT (e.g., 4o) prompt and add the following text to the prompt:
Analyze this stock - give me a unique perspective on whether it's overvalued or undervalued assuming a 15% discount rateStep 4: Wait for the stock analysis and use follow-up prompt — e.g., to find the implicit growth rate of the stock based on the current market cap:
Please figure out the growth assumptions implicit in the market cap assuming a growth period of 10 years and different growth rates until you find the growth rate assumed by the marketIn my case, ChatGPT figured out that given my 15% discount rate and a terminal 3% growth after 10 years, the market currently assumes a 42.77% implicit growth rate of free cash flows. Judge for yourself if you find this reasonable!

If you want a more fine-grained qualitative analysis, check out my valuation here:
 Valuing $NVIDIA as a Real Estate Company That Sells Housing to AI Agents ($100k/Share in 2034)
Valuing $NVIDIA as a Real Estate Company That Sells Housing to AI Agents ($100k/Share in 2034)
Be on the Right Side of Change
https://miro.medium.com/v2/resize:fit:1200/1*ddOciEHIZl4D-pKrpUDj7Q.png
In the evolving landscape of Software as a Service (SaaS), scalability and efficient resource management are paramount. This is where the concept of multi-tenancy steps in, serving multiple tenants with a single application. In this article, I’ll explain the basics of multi-tenancy in Laravel, demonstrating how this architecture can be a game-changer for developing scalable applications. This article is the first part of a series focused on multi-tenancy, starting with the basics and moving to more detailed implementations in future articles.
Multi-tenancy is a software architecture where a single application serves multiple users or customer groups, known as tenants. Each tenant’s data is isolated and remains invisible to other tenants. Essentially, multi-tenancy allows for sharing the same application and infrastructure while providing each tenant with a separate and secure environment. I call it a game-changer because it transforms how resources are utilized and managed, leading to more scalable and efficient systems.
In simpler terms, it’s all about the same software that multiple customers use, where each can see their own data, and it’s hosted in one place.
I highly recommend watching this insightful talk from 2017 on building multi-tenant applications, you can watch it here.
Definition: All tenants share a single database. Data from different tenants is differentiated by including a tenant_id on each relevant table.
Pros:
Cons:
Use Case: Best for small to medium-sized applications where the number of tenants and the volume of data are manageable, and the security requirements are not exceptionally stringent.
Definition: Each tenant has its own database, ensuring complete isolation of data.
Pros:
Cons:
Use Case: Recommended for larger applications where tenants require robust data isolation, have high data volumes, or need to comply with strict regulatory standards.
Definition: A mix of single and multiple database approaches where some tenants share a database while others have individual databases. This model is tailored based on tenant size, regulatory needs, or performance requirements.
Pros:
Cons:
Use Case: Ideal for applications with a diverse tenant base where different tenants have varying needs regarding scalability, security, and cost. For instance, startups or small enterprises in the same multi-tenant application might share a database, while large corporations have dedicated databases.
While having a multi-tenancy application offers numerous benefits, there are still challenges to consider, as mentioned below:
These challenges highlight the need for careful planning and robust system design to ensure the successful implementation of a multi-tenancy architecture.
I think it’s always good to see real-life examples, as they help you understand the concept better and assist in deciding whether you need it or not:
Laravel is well-suited for multi-tenancy because it offers robust built-in features like authentication, database migrations, and a powerful queue system, all of which simplify the management of multi-tenant environments. Additionally, Laravel’s extensive package ecosystem, including tools specifically designed for multi-tenancy, makes it easier to implement and maintain isolated tenant data and functionality within a single application framework. This, combined with strong community support, makes Laravel a practical and efficient choice for developing scalable multi-tenant applications.
Thank you for reading this article, which has covered the basics of multi-tenancy. In the next article, I will delve into a step-by-step implementation of multi-tenancy using a multi-database approach with the tenancyforlaravel package. Feel free to leave a comment with your thoughts or questions!
Laravel News Links
https://s3files.core77.com/blog/images/1541251_81_132216_Xd5gyrbNh.jpg
I’ve seen lots of craftspersons who can join wood to wood. But I haven’t seen many who can join wood to stone, with this kind of precision:





That’s the Wabi-Sabi bed, by furniture designer Ethan Stebbins. The wood is White Ash, and the stone is granite, which Stebbins harvested from coastal Maine, where he’s based.
Stebbins’ Dovetail Bench employs the same granite, and Douglas Fir:





And his Dovetail Stool uses granite and charred Cedar.






Stebbins describes his process:
"My work mainly relies on paying close attention to the organic matter’s properties. One must appreciate the individual characteristics of a certain wood kind or a certain type of stone before shaping them and joining the two together."

"There is a rather special moment when you carve, a quiet, flashing moment when the natural character of the stone reveals itself. This moment is everything."
Stebbins is represented by New York gallery Les Ateliers Courbet.
All images by Joseph Kramm.
Core77
https://www.ammoland.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/zbmlogihpsy-500×281.jpg
Building an AR-15 from scratch or enhancing an existing one can be a gratifying experience for any firearm enthusiast.
However, it’s a process that demands precision and awareness of common pitfalls. Steve and Caleb from Brownells delve deep into the crucial aspects of AR-15 assembly that can make or break your build. Avoid these mistakes on your next rifle build.
Mounting Accessories that Impact the Gas Block
One of the most common mistakes in AR-15 assembly is the incorrect mounting of accessories, such as bipods, that affect the gas block. This error can shift the barrel’s alignment subtly but significantly, compromising the rifle’s accuracy. To avoid this, it is crucial to select the attachment point carefully and use shorter screws if necessary to ensure that these do not exert undue pressure on the gas block.
Gas Block Alignment
Proper alignment of the gas block with the barrel’s gas port is essential for the reliable operation of your AR-15. Misalignment can result in cycling issues due to insufficient gas flow, leading to operational failures. When installing the gas block, ensure it is perfectly aligned with the gas port for optimal performance. This precise fit is crucial for maintaining the rifle’s reliability and longevity.
Over-Torquing the Castle Nut
While it might seem minor, applying too much torque to the castle nut can cause serious damage to the threads of the receiver extension or buffer tube. The recommended torque setting is 40 foot-pounds. Exceeding this can deform the buffer tube and other connected components, potentially leading to irreversible damage.
Excessive Material Removal in Upper Receiver Lapping
Lapping the upper receiver can be beneficial for ensuring a flush fit between the barrel and the receiver. However, removing too much material can result in the barrel sitting too far inside the upper receiver. This misplacement can affect feed ramp alignment and gas block positioning, which could lead to functional issues. Controlled lapping is necessary to achieve the right fit without compromising the structural alignment of the receiver.
Improper Buffer Tube Installation
The correct installation of the buffer retainer and spring is vital for the proper functioning of your AR-15. An incorrectly installed buffer tube can prevent the upper receiver from closing correctly, which could lead to operational failures. Ensuring that these components are installed at the proper depth is essential for their optimal performance.

|
Cmmg Ar-15 Parts Kit Hd Pivot & Takedown Pins |
Brownells.com |
$ 18.99 |
|
|
|
PSA AR15 Parts Replacement Kit |
Palmetto State Armory |
$ 12.99 |
|

|
PSA AR15 Parts Replacement Kit |
Palmetto State Armory |
$ 12.99 |
|
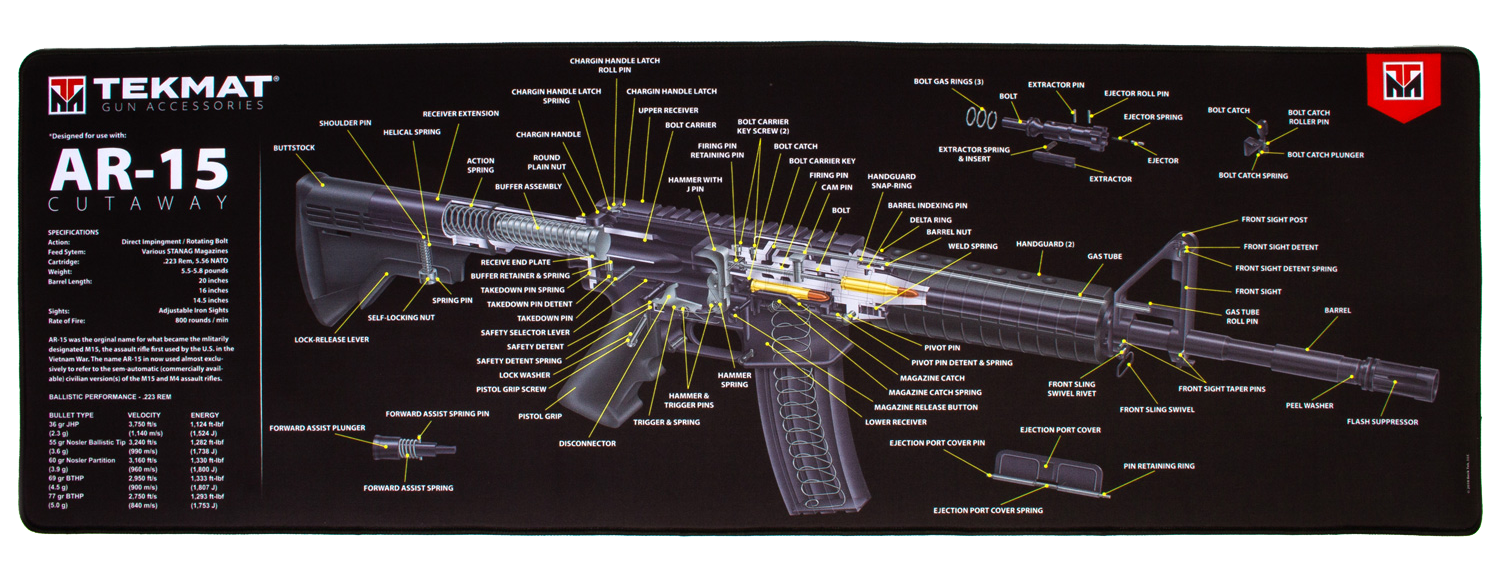
|
TekMat TEKR44AR15CA AR15 3D Cutaway Ultra 44 Cleaning Mat AR15 Parts Diagram 15 x 44 |
Ammunition Depot |
$ 21.99 |
|
Lock & Load
Building an AR-15 requires attention to detail and an understanding of the intricacies involved in its assembly. By avoiding these common mistakes, you can ensure the creation of a reliable and accurate firearm. Remember, every mistake is a learning opportunity. Share your experiences and tips within the AR-building community to help others avoid common pitfalls and enhance their building skills.
We encourage our readers to engage with the content, share their personal insights, and discuss their building experiences in the comments below. Whether you are a novice or a seasoned builder, there is always more to learn in the evolving world of firearm assembly.
AmmoLand Shooting Sports News
https://larafast.com/og-image/Larafast%20Fast%20Projects/Laravel%20based,%20ready%20to%20use%20projects%20made%20with%20LarafastLaravel News Links
https://theawesomer.com/photos/2024/05/raiseek_maintenance_mat_t.jpg
| Buy
This rubberized mat is ideal for maintaining firearms, knives, pocket tools, and mechanical gadgets. Its divided trays keep parts and tools organized, while magnetic panels in its top right corner keep metal parts from rolling away. Its soft polymer surface resists damage from oils and has a non-slip backing, while built-in hooks make it easy to hang and store.

The Awesomer
https://photos5.appleinsider.com/gallery/59642-121802-000-lede-Logic-Pro-d2-xl.jpg
Today’s iPads are capable enough to be used as full Digital Audio Workstations, but there’s also a range of audio editing apps for every need — and budget. Here are your best choices.
One thing that iPads are unexpectedly poor at is recording podcasts — they can’t readily be used to record a host and remote guest separately. There are workarounds but none that match the audio quality of being able to record directly.
Which is curious, because once a recording has been done, the iPad is nothing short of spectacularly capable at editing. There is simply a slew of audio editing apps available in the App Store — AppleInsider stopped counting at 60 of them.
Although at least one,Audacity, is really only on the iPad as a scaled-up iPhone app for people who like the Mac versions.
Alternatively, though, some of the apps claiming to edit audio are really meant for other media purposes and happen to include audio editing. A couple of those are worth looking at if you only rarely need to edit audio and you do already know these apps well.
That’s really how you decide between the apps. There is no limit now on what you can do with an iPad and the right app, but you always have to start with what your needs are — and what your budget is.
Even when audio isn’t their primary focus, there are very many apps that have to include at least some features for editing spoken word or music. The best examples of this are iPad video editors, of which there are now many.
DaVinci Resolve is a video editor, but it can also be used for just audio
Apple’s own iMovie is one, and it’s free for all iPad users. Equally, Apple’s other video editing app, Final Cut Pro for iPad 2 includes very many audio features for $49/year (or $4.99/month).
In this same line there is also DaVinci Resolve, which is free but includes optional in-app purchases. If it’s solely audio editing you want it for, you’ll never need its paid extras.
How, while all of these include at least basic and often quite powerful audio editing features, they are never the right choice unless you need their other functions. If you already edit video, for instance, then being able to quickly use tools to also do some audio editing in an app you’re familiar with is tremendous.
If you don’t already know, say, iMovie, then simply getting to its audio editing features will be a chore.
When you don’t know apps like that, and when you need to do more than one or two quick audio pieces, then you need an audio editor. In AppleInsider‘s experience, there are three audio apps that are worth considering.
Apple’s GarageBand is designed first for recording voice and musical instruments, and then for adding music loops. But once you’ve done all or any of that, you have to be able to edit the audio.
Consequently, GarageBand comes with a multi-track audio editor. That means you can, say, have two podcast guests recorded separately and then line them up together.
GarageBand. Note the one-size-fits-all "Fade Out" control
GarageBand also lets you split tracks, so you can cut out sections if you need. There are also features such as fading in or out, although overall, GarageBand tends to prefer ease of use over fine control.
So when you need more, or GarageBand’s settings don’t happen to suit what you want to do, it’s time to buy or subscribe to an audio app.
Ferrite is an example of where a list of features doesn’t convey all of what’s good about it. For instance, it has multi-track editing, but so does GarageBand.
Yet in Ferrite’s case, manipulating those multiple tracks just feels easier. And there are specific features such as the ability to tell it to automatically dip one track as another is playing.
Multiple audio tracks being edited in Ferrite for iPad
Ferrite is also an example of an app whose free version is excellent enough that you upgrade at least in part just to reward the developer. Nonetheless, if you do upgrade to the Pro version for $30, you do get extra features.
Such as the ability to play back at twice normal speed as you edit. Or the ability to tell Ferrite to strip out accidental silences, for instance when you’ve misaligned two vocal tracks and inadvertently left gaps.
The Ferrite Recording Studio requires iPadOS 16.4 or later.
As shown off by Apple at its "Let Loose" event as a highlight of the iPad’s capabilities, Logic Pro is surely the single most powerful and comprehensive audio editor available for the iPad. On the Mac, it has competition from Pro Tools and to a lesser extent Adobe Audition, but neither are available on the iPad.
It’s a true Digital Audio Workstation (DAW) and as such is right for musicians, producers, and audio engineers. Logic Pro is really extreme overkill if you’re doing much less than making albums.
Yet even if all you want is to record a podcast with two hosts, having a full-on DAW at your fingertips is superb. It does come with the cost of a fairly steep learning curve, though, simply because it does so much.
It’s also arguably expensive, or at least it is not a casual purchase. Following a month-long free trial, Logic Pro for iPad costs $49/year, or $4.99/month.
Logic Pro for iPad 2 requires iPadOS 17.4. Apple has not yet specified any minimum hardware requirements for the forthcoming new version, but Logic Pro for iPad 1 needed an iPad with an A12 Bionic chip or later.
It also takes up quite a significant amount of storage space. The app itself is 1GB — compared to Ferrite’s 25MB — but then there are optional extras that can swell that to 15GB.
Editing an audio track in Logic Pro for iPad
The AppleInsider podcast used to be edited on Ferrite, but it’s now done on Logic Pro — albeit for the Mac. The Mac edition is a one-off $199 fee and it does not come as part of the iPad version’s subscription.
That’s the same as with the other app that Apple highlighted at its iPad event, Final Cut Pro. But unlike Apple’s video editor, Logic Pro has the tremendous benefit that projects can be moved between iPad, Mac, and back again, as you need.
The one you want is Logic Pro for iPad — if you’re going to use it enough to warrant the subscription cost. And if you’re going to be using it for either complex enough projects, or just so many of them that it’s worth the time it takes to learn Logic Pro.
Then at the other end of the scale there is GarageBand, which you’ve already got. The fact that it’s designed for musicians means it has a lot of recording and loop features that you might not need, though, and its controls tend to be more basic.
So the sweet spot across all of the audio editor apps that AppleInsider has used, is the Ferrite Recording Studio. This, too, takes some time to learn but not as much as Logic Pro.
There may be situations where it becomes an issue that there isn’t a Mac version of Ferrite. But overall, it just means that the developer is truly focused on making it the best it can be for iPad users.
Whichever app you use, though, it’s got to be said that editing audio on an iPad is a pleasure. It’s much more of a pleasure to edit it than it is to record on, but pinching in and out of a track’s timeline, it feels like you’re touching your music and vocals.
AppleInsider News